Posted 2019/9/23
In order to measure a very small current signal, it is important to use a low-noise I/V amplifier. In addition, it is important to set up appropriate measurement equipment under optimum measurement conditions. Be aware of the following points when measuring very small current signals.
It is necessary to pay attention to the following two points.
In order to detect a very small signal, it is important to minimize the effect of external noise. The following measures are recommended to reduce the effect of external noise.
Generally, as Cs of the current amplifier increases, the following effects occur.
Regarding the (a)
Please refer to "Stable against sensor
capacitance".NF SA-600 series achieves stable current amplification regardless of Cs.
Regarding the (b)
Increase noise is explained by using the circuit diagram (shown in Fig.8) of a general current
amplifier and a graph of input-referred noise current (shown in Figure 9). As shown in the
Fig.9, input equivalent noise current increases as frequency increases, and it attenuates when
the upper cutoff frequency is exceeded. If Cs is large, the noise level increases because the
input equivalent noise current starts to increase from lower frequency.
The output-noise waveform of SA-607F2 (LPF setting: THRU) when Cs is 10 pF and 1000 pF is shown
in Figure 10. This shows that output noise increases more than 10 times when Cs becomes 100
times larger. Thus to measure very small signals, it is important to reduce noise by reducing
Cs.
The following is effective for reducing Cs.To select a sensor with a small capacitance.
To be shorten the wiring length from the sensor to the current amplifier as much as possible.
To select a cable with a small capacitance (cable with a characteristic of high impedance). As
reference, table 5 shows relationship between BNC coaxial cables and their capacitance. Typical
commercial coaxial cable has a characteristic impedance of 50 Ω or 75 Ω. Using the
short cable is the most simple method to reduce Cs.
Figure 9: Circuit diagram of typical I/V amplifier and input-equivalent current noise
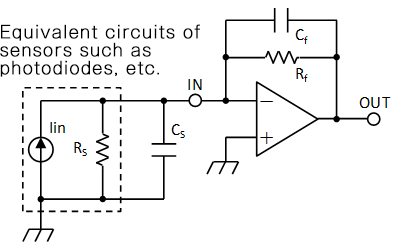
(a) Simplified circuit diagram of an I/V amplifier
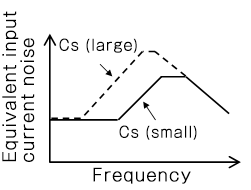
(b) Frequency characteristics of equivalent input current noise
Figure 10: Output noise voltage waveform depending on Cs
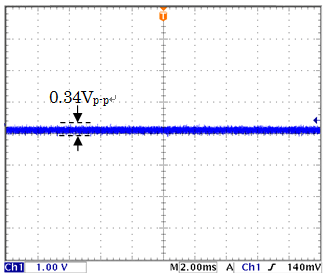
(a) Cs=10pF
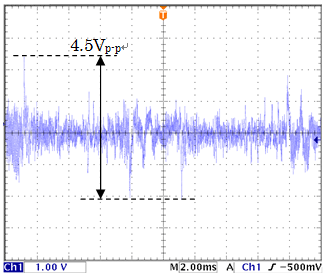
(b) Cs=1000 pF
Table 5: Types of BNC coaxial cables and their capacitance
| Characteristic impedance | Coaxial cable | Capacitance |
|---|---|---|
| 50Ω | 3D-2V etc., RG-8/u, etc. | About 100 pF/m |
| 75Ω | 3D-2V etc., RG-11/u, etc. | About 67 pF/m |
| 95Ω | RG-22/u, etc. | About 53 pF/m |
| 125Ω | RG-63/u, etc. | About 33 pF/m |
Related keywords : Ultra low noise amplifier, LNA